Setting the Stage for Automation's Future
Automation is rapidly changing how businesses operate, making processes faster, more accurate, and more cost-effective. As we look to the future, all signs point toward more intelligent, autonomous solutions that can learn and adapt on their own.
Introducing AI Agents, the newest evolution in automation technology.
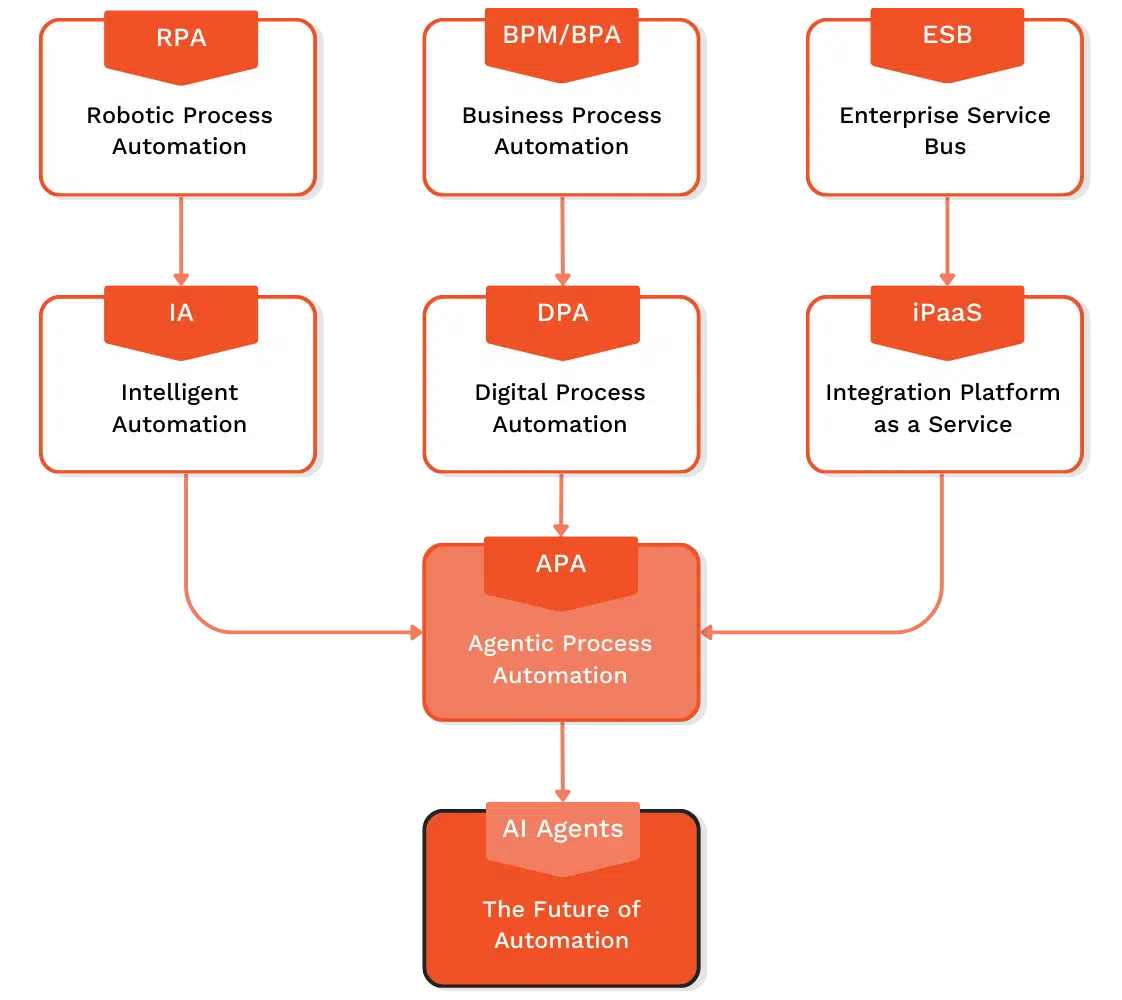
Firstly, let’s get into the building blocks of modern automation—such as RPA, BPM/BPA, ESB, IA, DPA, and iPaaS—and show you how they converge into Agentic Process Automation (APA) before finally advancing to AI Agents.
This blog will take you through what each of the automation components are and why they matter, where leading automation platforms (UiPath, Nintex, Microsoft Power Platform, Microsoft Fabric, ABBYY) fit in and why AI Agents represent the next evolution in delivering intelligent, self-governing processes.
The Building Blocks of Automation
RPA (Robotic Process Automation)
- What it is: RPA uses software “bots” to perform repetitive tasks—like data entry or invoice matching—exactly how a human would interact with software.
- Why it’s relevant: It frees up teams from mundane tasks, speeding up processes and reducing human error.
- Example: Automating invoice processing: A bot logs into accounting software, checks invoices, and updates payment statuses.
- Where the platforms that we work with fit in:
- UiPath and ABBYY are heavily used here—UiPath for the RPA orchestration, and ABBYY for intelligent document capture and text recognition.
BPM/BPA (Business Process Management / Business Process Automation)
- What it is: BPM/BPA focuses on defining, managing, and optimising the broader workflows within an organisation—beyond just individual tasks.
- Why it’s relevant: Provides visibility and structure around entire processes, ensuring every step is efficient and compliant.
- Example: End-to-end purchase order approval processes with clear stages, approvals, and handoffs to humans.
- Where the platforms that we work with fit in:
- Nintex and Microsoft Power Platform offer drag-and-drop tools to automate these business workflows while integrating with various systems.
ESB (Enterprise Service Bus)
- What it is: An ESB is a software architecture model that helps different applications within an organisation communicate securely and reliably.
- Why it’s relevant: Ensures data flows seamlessly between systems—no matter how diverse they are—so that automation can happen end-to-end without manual data transfer.
- Example: Integrating CRM, ERP, and HR systems so that an employee onboarding process triggers automatically across all platforms.
- Where the platforms that we work with fit in:
- Microsoft Fabric (particularly its integration capabilities) can play a role in connecting data sources and cloud services securely.
IA (Intelligent Automation)
- What it is: IA merges RPA with artificial intelligence or machine learning capabilities to handle tasks that require some level of cognition.
- Why it’s relevant: With AI, automated tasks become more adaptable, able to handle variations and more complex decision-making.
- Example: Sorting customer emails based on sentiment or urgency, then routing them automatically to the correct department.
- Where the platforms that we work with fit in:
- ABBYY for intelligent document understanding; Microsoft Power Platform and UiPath also incorporate AI modules for tasks like sentiment analysis and image recognition.
DPA (Digital Process Automation)
- What it is: DPA is a holistic approach to transforming manual and paper-based processes into fully digital workflows.
- Why it’s relevant: It goes beyond simple task automation, focusing on re-engineering processes to be entirely digital.
- Example: A fully digitised loan application process that moves from online forms to credit checks to final approvals without physical paperwork.
- Where the platforms that we work with fit in:
- Nintex, Microsoft Power Platform, and UiPath can all help build fully digital workflows with low-code and no-code solutions.
iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service)
- What it is: Cloud-based platforms that standardise and simplify how organisations integrate different applications and data.
- Why it’s relevant: Allows quick, scalable connections between on-premise and cloud systems, facilitating the flow of information for automation.
- Example: Automatically moving customer data between a CRM in the cloud and an on-premise billing system.
- Where the platforms that we work with fit in:
- Microsoft Fabric can serve as a scalable data and integration platform, enabling real-time or near real-time data synchronisation.
From Building Blocks to Evolution: Agentic Process Automation (APA)
Agentic Process Automation takes these fundamental automation tools (RPA, BPM, IA, etc.) and combines them into an orchestrated framework. The result is an automated system that not only follows rules and workflows but can adapt to complex, multi-departmental processes.
- Why it’s the next evolution: APA adds more autonomy to automation by linking intelligent bots with business processes and seamless integration. For example, a large-scale invoice processing workflow can proactively escalate exceptions to a human only when it detects anomalies or compliance risks.
The Future Is Here: AI Agents
After APA, the next natural step is AI Agents—fully autonomous software entities that can sense, reason, and act in dynamic environments with minimal human intervention.
- How they work: AI Agents leverage advanced machine learning and natural language models to interpret data, learn from outcomes, and adapt their approach.
- Real-world example: A customer service AI Agent that independently engages with customers across multiple channels (web chat, email, social), learns common pain points, and escalates only unusual queries to human agents—continually optimising responses as it gathers more data.
- Why they’re game-changing: By blending self-learning, decision-making, and automation in real-time, they reduce overhead costs, increase accuracy, and free up your workforce to focus on higher-value tasks like innovation and strategy.
Conclusion
At Tecala, we’ve seen first-hand how embracing each phase of automation landscape — from foundational RPA and BPM up to cutting-edge AI Agents — can transform organisations.
We specialise in UiPath, Nintex, Microsoft Power Platform, Microsoft Fabric, and ABBYY, bringing together all the necessary pieces for a successful automation journey.
If you’re ready to explore what AI Agents could do for your business, get in touch with us today and let’s embark on the next phase of your automation evolution.